
- NEWSLETTER,U.A.E
- February 8, 2023
Foundations and Trusts are established to provide financial support for intended organizations and individuals through the management of assets and family wealth. Though both these are legal entities, they differ from each other in structure, asset control, and liability.
Structure
The primary difference between a foundation and trust lies in its structure. A foundation is not legally allowed to undertake commercial activities for generating profits and is managed and controlled by a Member council like a Board of Directors. It is usually funded by a single family or individual to protect family wealth and make further investments. The founder registers the foundation’s charter at the public registry which can sue or be sued, can enter into contracts and agreements, can open bank accounts, and engage in commercial activities. It is governed by by-Laws, similar to an AOA. UAE law offers a modern and flexible legal framework as DIFC foundation law, for establishing private, charitable, and corporate foundations.
Trusts are established to relate three entities including the settlor that creates the trust, the trustee who is in charge of the trust, and the beneficiary that gets benefits from the trust. The legal ownership of the trust remains with the trustee that holds and manages assets on behalf of one or more beneficiaries. Trusts are usually private arrangements and are not governed by public disclosure requirements but by a trust agreement, defining the responsibilities and rights of the trustee and beneficiaries. The two main types of trusts in the UAE are charitable trusts and discretionary trusts.
Assets and Wealth Control
The level of control over assets and wealth differs between trusts and foundations. In general, foundations have more control over family assets and can undertake specific programs or initiatives as documented in the charter and by-Laws as per the objectives of the Founder in generating returns from investments.
Trusts have limited control over family assets and can use the assets only for beneficial owners. Trusts are typically established for specific organizations and individuals wherein trustees are made responsible for managing the assets.
Liability
Foundations are established with limited liability where the personal assets of the beneficiaries and members of the council are protected. The founder has no legal claim to assets.
The trustee is fully responsible for the liabilities of the trust unless a protector is accepting the liability.
The Takeaway
Both UAE nationals and expatriates establish Foundations and Trusts to help them manage their assets. Both are useful vehicles for managing and protecting family wealth and enjoying tax exemptions. DIFC doesn’t impose any withholding tax on dividends, interest, or royalties paid to UAE non-residents. Incomes generated within the DIFC are also tax-exempt. While setting up a Foundation or Trust, hiring the services of a law firm is usually recommended.

- NEWSLETTER, GLOBAL
- January 10, 2023
Today, it is not only high volume, repetitive, manual, and time-consuming tasks that are outsourced, even strategic tasks having competitive advantage are also being offloaded to outside third parties for achieving higher profits as in the case of contract research and contract manufacturing organizations (CRO/CMO) in the pharmaceutical industry.
When any business begins to grow, it can be difficult to manage everything in-house. Outsourcing allows businesses the time and resources necessary for focusing on other more important aspects of the company, while still offering customers high-quality products and services for enhanced business profitability.
Previously, it used to be non-core business functions that used to be outsourced in most cases. However, as the definition of core and non-core business functions are getting subjective, the outsourced functions are normally varying from business to business. However, a business can opt for the following six key business functions for outsourcing for clocking higher profit margins.
HR OUTSOURCING
Some HR functions are time-consuming and repetitive and put a huge cost burden on a company. To save money and time, you can enter into a contractual agreement with an external third-party provider whereby you transfer the responsibility of managing certain HR functions to the outside party. Many types of HR outsourcing options are available to you today.
Training, counseling, recruiting, and administering are some of the functions that many organizations prefer to outsource for reducing costs. Professional HR outsourcing services due to their expertise in this field and access to the latest technologies can even automate these HR functions and provide high-quality services at a significantly lower cost.
ACCOUNTING & BOOKKEEPING OUTSOURCING
Accounting and bookkeeping outsourcing is an arrangement where an external team of skilled accountants carry out the entire accounting tasks and provide a complete accounting and bookkeeping solution.
Setting up a skilled in-house accounting team can be expensive and difficult, and many companies opt for outsourcing this business function. The standard accounting services that are outsourced are Payroll processing, Bookkeeping Services, Tax returns filing, Financial statement preparation, Invoice processing, Financial planning & analysis, Cash flow management and Accounts receivable and payable management.
Besides cost savings, other top benefits of outsourcing accounting are an industry trend and one of the most popularly outsourced functions for SMEs. Businesses benefit a lot from outsourced finance and accounting services due to lower operating costs, improved accuracy and effectiveness of finance and accounting data, better financial decision making, and zero regulatory non-compliance. It is projected that over the next 4-5 years, the market for finance and accounting outsourcing globally would grow to USD 53.4 billion at a CAGR of 5.9%.
Today new age digital technologies have significantly eliminated most of the manual accounting tasks and made finance and accounting processes more simplified and automated. When outsourced, SMEs can have access to such technologies at a lower cost than arranging infrastructure and resources internally for the needed technological tools. Most of the IT services are outsourced by banking and financial institutions and toward upgrading and automating finance and accounting functions.
Outsourced accounting and finance can result in huge monetary savings for SMEs besides saving time, reducing financial paperwork, and better utilization of human capital. The top benefits of outsourcing accounting services include reduced compliance risks, time-saving, scalability, automation, and advisory.
MARKETING OUTSOURCING
When in-house marketing skills and talents are scarce and your marketing team is struggling to make the marketing campaigns to fruition, outsourcing marketing tasks to a specialist third party can take off huge operational pressures your team might be enduring. Marketing normally involves lots of different tasks stretching from advertising, content creation, campaign management, tracking effectiveness, and many more.
However, to be effective, marketing needs to be innovative and engaging, and when outsourced can connect you with marketing agencies who specialize in keeping on top of new technology and trends.
Marketing outsourcing can help you get an outsider’s perspective of your business and bring new and exciting marketing ideas. A salaried in-house marketing team is expensive and in the case of outsourcing you only need a budget when it’s necessary.
Outsourced marketing services can provide you with marketing software that can automate and schedule various tasks, such as content creation, email marketing, and social media posting to name a few.
IT OUTSOURCING
IT outsourcing is defined as a practice where an external service provider is engaged to deliver some or all of the IT functions required by a business including managing infrastructure, preparing strategy, and running the service desk.
IT outsourcing is common for small businesses that don’t have the ability and affordability to manage an in-house IT staff and infrastructure. Outsourced IT firms due to their skills, resources, and expertise can often offer more efficient services than in-house IT teams and can manage a wide spectrum of IT tasks.
ADMINISTRATIVE TASKS OUTSOURCING
Effective management of administrative tasks needs lots of time and organizational skills and usually includes scheduling appointments, answering customer queries, appeasing dissatisfied customers, receiving orders, and many other communication tasks.
Outsourcing these administrative tasks to an independent contractor or virtual assistant can help you eliminate manpower costs.
THE TAKEAWAY
Outsourcing always brings a competitive advantage through cost reduction, enhanced staffing flexibility, and time savings. Outsourcing business functions is a rising trend and businesses expect to spend billions of dollars annually on outsourcing.
However, there is one note of caution when services are outsourced. Frequently changing outsourced service providers can disrupt business continuity. Secondly, a company is more likely to build a strong relationship with its outsourcing service provider when working with the same team for a longer period resulting in an increased commitment and trust.

- NEWSLETTER, GLOBAL
- January 10, 2023
Survey reveals that in today’s competitive business climate, engaging and retaining the best talents is the topmost priority of the corporate world. There is a growing trend amongst companies to hire global talent in order to meet this objective.
Employee hiring is challenging, and more so in a global context given the geographical limitations, cultural differences, and complex and ever-changing labor laws.
Moreover, once hired, the employer must ensure that the relocation of the employee is comfortable and stress-free. Hence global recruitment strategies need to be effective so that crucial positions are adequately and timely filled in.
Following are the seven tips that can help large companies recruit globally in an efficient manner.
EMPLOYER BRANDING
For global hiring, employer branding must be a priority for all companies as most job seekers consider a company’s reputation and branding before applying for a job. Moreover, a strong employer brand brings down the cost of employee turnover drastically.
An organization can communicate its visions, mission, and values to the target audience and help prospective employees collaborate with the organization over their competitors.
For global hiring, developing a global employer brand is very much a necessity to attract talent. Job seekers must be able to access the company’s website easily and discover that it is an attractive place to work. The company must have a strong social media presence through LinkedIn, Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook and provide company reviews from existing employees on its website.
HIRING A GLOBAL PEO/GLOBAL EOR
Hiring professional global manpower sourcing services like an Employer of Record (EOR) or Professional Employer Organization (PEO) can greatly facilitate global hiring and paying employees nearly anywhere in the world, in full compliance with tax and labor laws.
When a business entity in its expansion drive looks for setting up a subsidiary in another jurisdiction, global EOR/PEO Services can be an effective way to hire employees as onboarding of an employee can be done on short notice and then transferred to the subsidiary.
OUTSOURCING A GLOBAL PAYROLL COMPANY
Most global companies find it hugely burdensome to pay staff in other countries in full compliance with local employment and tax laws and especially so when such recruitment drives span over multiple countries having multiple currencies and varied pay rules.
If a global payroll company is outsourced on a monthly settlement basis, the payroll company will shoulder the responsibility of paying all your staff on time and in compliance with all applicable tax and labor laws.
IDENTIFYING TARGET LOCATION
The strategy for global hiring, especially for large companies, needs to be directed to identifying target countries where the likelihood of finding job-specific talent pools is maximum. This will reduce time and money in looking for the most appropriate talents.
Countries which are having significant labor populations with specific skill sets as in the case of Bangladesh, India, and Poland where talented software professionals can be found in plenty. Even long-term employee costs could be put in check as manpower sourcing
from such selective countries may cost lower.
LEVERAGING TECHNOLOGY
Implementing company-wide recruitment software can facilitate the global sourcing of manpower. Today technology may play a decisive role in laying down a company’s global recruitment strategy. Centralized technology for tracking recruitment data across different time zones improves strategic decision-making.
A global system may be deployed to remain compliant with the latest immigration policies and data privacy rules in different countries.
Recruitment utilizing AI is also becoming increasingly popular as it can optimize tedious and repetitive tasks.
An AI scanner can scan resumes and cover letters to highlight the candidates with the most potential. A company can even use AI to assess past job descriptions to create a valuable recruitment database for future use. AI chatbots can help communicate with applicants and schedule interviews.
THE TAKEAWAY
The Covid pandemic has made remote work our new normal and as per the study, this trend will continue in the future, especially in countries with advanced digital infrastructure. This rising trend of remote working has increased the potential of global hiring.

- NEWSLETTER, GLOBAL
- January 10, 2023
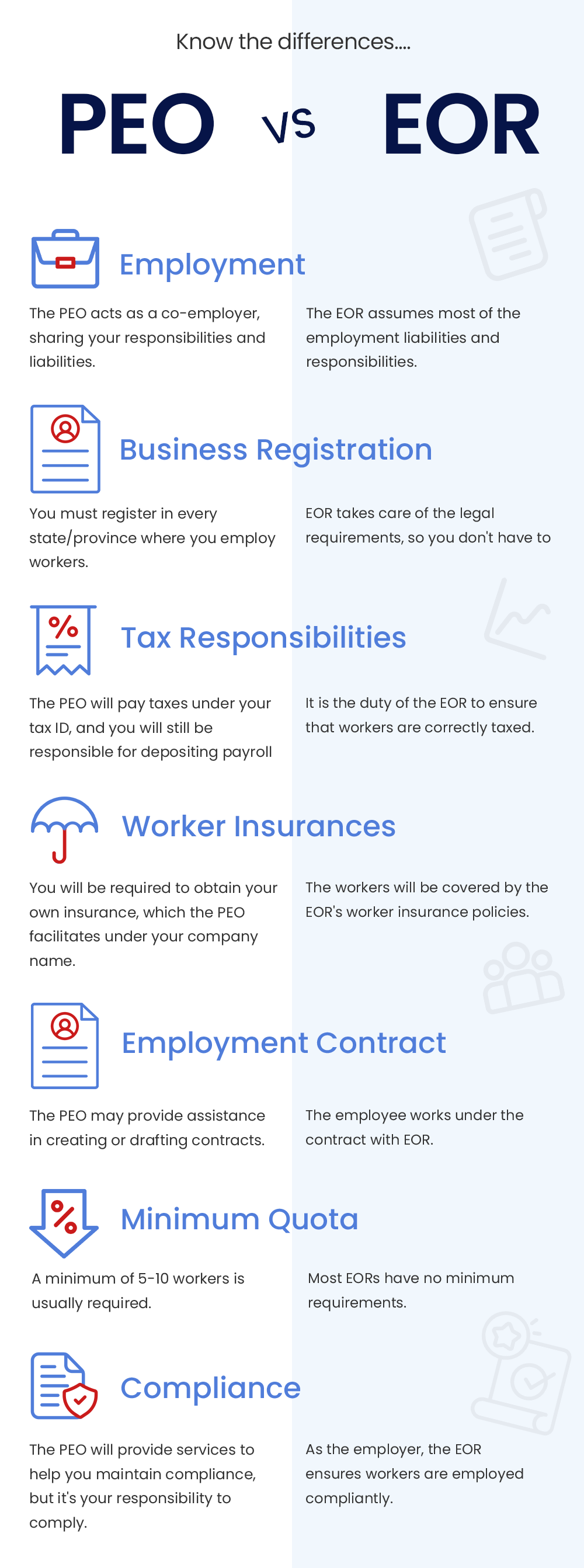
Employer of Record (EOR) and Professional Employer Organization (PEO) operate like business partners and help companies manage teams across the world. While a PEO acts as a co-employer, an EOR is the legal employer of the distributed workforce of an organization. A clear understanding of a PEO versus EOR is the first step in rightly choosing one out of these two for your company’s complex needs of managing the human capital.
Both the EOR and PEO provide Global Mobility Solutions, however, an EOR as the legal employer does much more than just manage HR outsourcing. Overseas employment is the main function of an EOR that is achieved by removing international barriers to business expansion by using its robust network of local entities across the world.
An EOR
Effectively managing the HR, legal, tax, and local compliance requirements of your employees is the primary domain of responsibilities of an EOR in any country where your organization doesn’t have any legal representation.
Organizations planning to quickly and compliantly hire employees can do so through their EOR partner as it provides the organizations with flexible and cost-effective entry into any market without requiring any business registration.
Hiring an EOR partner makes you stress-free and allows you to focus on the core responsibilities.
The Working of an EOR
Once an organization makes a partnership agreement, the EOR is allowed to employ the staff through its local entity legally. An EOR can onboard, provide global payroll solutions, manage taxes, ensure payroll compliance, and carry out benefits administration including unemployment claim reporting on your behalf, be it a three-month assignment or a permanent position. EOR becomes your legal employer while you remain the managing employer.
A PEO
A Professional Employment Organisation (PEO) is a company that mainly partners with SMEs and provides HR services for full-time, permanent employees.
HR services that are provided include payroll processing, benefits administration, regulatory compliance, and tax filings.
International PEOs operate as a company’s outsourced HR department so in-house teams have more time to focus on their core functions.
A PEO is a partner company and not the employer of your workforce. Partnering with an international PEO can relieve an organization of its HR responsibilities, however, the organization is still held accountable for both legal and day-to-day operations including registering your business in the jurisdiction where you hire staff.
Working of a PEO
A PEO acts as a co-employer and when you outsource the services of a PRO, you enter into a co-employment agreement of contractually allocating and sharing your HR responsibilities and liabilities. This gives you legal insurance that the PEO manages part of your HR requirements and only alleviates part of the HR risks.
Difference Between an EOR and a PEO
Both an EOR and a PEO handle HR functions for your company, however, these two are not the same. The five major differences that separate these two entities apart are outlined below.
Structure
Structurally a PEO is a co-employer while an EOR is a full legal employer having a direct employment model.
When you hire a PRO, you remain the main employer with authority over HR-related decisions. However, with an EOR who is your trusted partner with local expertise, you need to give up some authority and control over HR-related decisions.
Scope
While PEO services outsource your HR activities, EOR services take over your HR responsibilities as the employer. Hiring a PEO doesn’t absolve you of your responsibilities of complying with location-specific labor laws.
Scale
As PEO acts as a co-employer to manage HR-related tasks, it helps create more value for companies with more full-time rather than temporary employees.
In contrast, an EOR provides more flexibility to companies that rely on temporary employees or that need access to talent in other locations. There are no minimum employees for an EOR and even a few staff hiring assignments may be given.
Risk
A PEO being a co-employer, cannot lessen your employment liabilities and HR risks and can only manage and share them.
However, if an EOR acts as the actual employer of your workforce and assumes all employment risks and liabilities, your HR risks are reduced.
Cost
The hiring of PEO and EOR services involves both short-term and long-term costs. Both these services usually charge either a flat monthly fee based on employee headcounts or charge a percentage of monthly payroll expenses. Sometimes PEO services also demand a one-time introductory charge before rendering the services.
Global EOR Services generally cost less than a PEO in the long term as it covers insurance and benefits for your distributed workforce, saving time and money for your organization. With global PEO services, you would still be responsible for benefits and insurance.
Should You Choose an EOR or a PEO for Your Organization?
Lots of factors come into play when choosing between an EOR and a PEO. Hiring a PEO is ideal when all employees are in a single location, however, with the company expanding outside to other locations, it becomes entirely challenging.
An EOR is legal and can operate in many countries across the world to address your human capital needs. If your business wants to employ staff globally, then PEO is not the right solution.
Businesses eyeing new overseas markets need agility, cost awareness, and expertise. Generally, when a company goes global, complexities abound due to unfamiliar labor laws and regulations and the company needs a trusted partner like an EOR to successfully cross over the barriers to global expansion and realize optimum revenue growth.

- NEWSLETTER,U.A.E
- January 9, 2023
In recent years Dubai and the UAE are witnessing elevated FDI inflow, mostly driven by a friendly business environment, excellent infrastructure, pro-business policies, and structural reforms focused on diversification of the economy and building of a dynamic and ever-expanding private sector.
Attractive capital markets for foreign entrepreneurs and investors have also helped propel the growth in FDI inflow. As the investors are bullish and confident on the capital markets of Dubai and other emirates, fundraising for startups and scaleups is becoming easier.
As entrepreneurs go global, fundraising through foreign participation becomes more competitive unless international investors and entrepreneurs find the country or region attractive for investment.
Dubai and the UAE in the MENA region are seen to be the front runners in attracting FDI primarily due to a stable economy, tax incentives, and the existence of several free zones.
Why FDI for Economic Stability, Resilience, and Sustainability
Besides being a key driver of economic growth, FDI has always remained a significant non-debt financial resource for a country’s economic development. Foreign investors and entrepreneurs invest in a country to benefit from the investment privileges the country offers. The Dubai government in the recent past has signed more than 100 agreements to secure and facilitate foreign investments.
FDI helps the country develop technological know-how and generate employment. These investments have been pouring into Dubai and the UAE because of the vibrant business climate, the government’s supportive policy framework, and rising global competitiveness.
Data reveals the fact and bears the testimony that Dubai and the UAE are ahead of other MENA countries in terms of FDI inflow. The UAE contributed more than 30 percent of FDI inflow into the MENA region during 2020 and 2021 taking Dubai and the other emirates at the top of the list. The 2022 UNCTAD World Investment Report also reveals that the UAE ranks first in FDI inflows amongst the West Asian countries registering a phenomenal FDI growth of 4 percent and above.
What Attracts Foreign Investors
When foreign financial institutions or companies or governments want to invest, they often look for the economic stability of businesses or projects they are interested in. Besides, such investors focus on governance frameworks that offer transparency and tax efficiency.
Records of economic growth and prospects of economic growth and stability also matter a lot to foreign investors as these instill confidence amongst them. The availability of a highly-skilled workforce also adds to the investors’ confidence in facilitating fund inflow through new company formation in Dubai.
Why FDI is Flowing in Dubai
Dubai, including the other emirates, has attractive capital markets with a lower cost of investment for foreign investors across a lot of sectors. The UAE, as a whole, also symbolizes the political and economic stability investors long for. Dubai is preferred amongst other emirates due to its status as an International financial hub with an expanding and thriving business community. It is also one of the richest and smartest global cities with a high quality of life and high standards of living that global investors get attracted to.
Dubai’s strategic location also adds another feather to its crown as it is at the heart of the MENA region and connected to more than 240 cities worldwide by air. Besides, the city can boast of one of the best transport infrastructure facilities in the world.
International Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investors are also feverish about Dubai after the city rolled out the Dubai Metaverse strategy. As the digital drive picks up speed in the city, doing business is becoming easier. Besides, the Dubai government’s Paperless strategy and adoption of a technology-based unique approach towards measuring, impacting, and sustaining happiness for the entire city are causing investors to flock to the city.
The other reason that is driving investors to Dubai is the ease of doing business. Business registration for a business set up in Dubai is a straightforward process and only takes a few days.
The business community of foreign investors has established proven businesses and family offices in Dubai which is inspiring prospective investors to come and set up a business in the city. Business sectors that are offering the highest stability and growth potential include e-commerce, real estate, insurance, financial services, manufacturing, mining and tourism, and hospitality.
The other most vital reason for investors to choose Dubai is the number of dedicated free zones available in the city specifically designed to support and cater to specific business activities that enable foreign investors to obtain full business ownership. There are more than 40 free zones in Dubai, and some are solely dedicated to research and development.
Business registration and visa issuance processes are transparent and streamlined with easily available low-cost office spaces and warehouses.
Dubai is known as a tax haven and even after the introduction of corporate tax, a business with turnover surpassing AED 375,000 only needs to pay tax on profits and that too at a low rate of 9% which is one of the most competitive tax rates globally.
Foreign investors conducting business activities outside of the UAE don’t come under the corporate tax regime and foreign businesses owned by overseas investors in the free zones continue to enjoy tax holidays subject to fulfilling certain conditions.
The UAE has also signed several double taxation avoidance agreements (DTAA) with different countries which protect Dubai-based companies and individual residents from double taxation. As opposed to the tax systems in other jurisdictions, the UAE and Dubai governments don’t impose any tax on individual income from employment facilitating easier talent engagement and retention.
The Prospect of FDI in Dubai
In connection with the future FDI prospect of Dubai, Sheikh Hamdan bin Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum remarked, “We remain committed to enriching Dubai’s enabling business environment to explore fresh growth avenues with our partner investors to achieve even greater success in years to come. Furthermore, diversifying the economy, attracting more investment in future-focused sectors, and enhancing growth opportunities in the digital economy will remain our strategic objectives for Dubai’s development journey.”
Dubai and the UAE as a whole, are dedicated to investor services by creating business opportunities and protecting foreign investments. The UAE at the recently held Emirates Investment Summit announced the launching of projects under the ‘Project of The 50’ program that clearly outlined the next phase of growth in the country.
The primary goal of attracting increased FDI inflow into the country is to channel investment funds with public and private organizations. The nation aims at attracting a whooping AED 550 billion in FDI over the next nine years which is a tempting proposition for all startups and SMEs.

- NEWSLETTER, U.A.E, INDIA
- January 9, 2023
The year 2022 ended on a sweet note for both UAE and India as it witnessed the signing of a historic CEPA between the two with improving bilateral relations on both the economic and political fronts. In 2022, after the USA and China, the UAE became the third largest trading partner of India with bilateral trade exceeding USD 88 billion between the two countries.
Almost 40% of the UAE population is Indian and the ambitious digital infrastructure drive coupled with the growing technology startup incubation in the country is all set to attract more Indian tech talents and investors for Company Formation in Dubai, UAE. The recent initiatives undertaken by the UAE government including the issuance of Golden visas and long-term visas to freelancers in the tech field are seen as added catalysts fueling tech talent migration from India to the UAE.
The recently held GITEX Global show in Dubai during the middle of October 2022 also witnessed a huge response from Indian technology startups who displayed AI-powered solutions for creating multilingual videos of digital avatars including several technological innovations in health tech, blockchain, big data, IoT, metaverse and Web 3.0.
Dubai is also aggressively promoting the latest technologies in coding, big data analysis, virtual and augmented reality and human-machine interaction to drive the future for realizing the vision of Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, the Ruler of Dubai. Today, Dubai is a city of big data specialists and coders making it a global hub for
the metaverse community.
With the building of the Museum of the Future, Dubai UAE has conveyed to the world that the country has embarked upon its relentless futuristic journey of flying digitally high and exploring celestial bodies. Emirates space agency has already launched the Moon and Mars missions and is now planning for an interplanetary mission of landing a spacecraft on an asteroid.
“We want the UAE to become the world’s most prepared country for Artificial Intelligence,” said His Highness Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, Vice-President and Prime Minister of the UAE and Ruler of Dubai and announced on Twitter regarding his plans for the Centennial 2071 project. The UAE first rolled out Strategy for Artificial AI in 2017 which is considered to be the first mega project to achieve the objectives of the UAE Centenary 2071 to make all government services, sectors, and infrastructure projects rely on AI focusing on the economy, education, government development, and community cohesion.
The UAE AI strategy has placed the country at the top of the region for its readiness to adopt AI and will attract increased investments in the latest AI tools and technologies for promoting more effective governance and achieving 100% utilization of AI in government services and data analysis.
Dubai also plans to lead other emirates in 3D printing by 2030 and come out as a role model in all areas of science and innovation. By 2030, the city wants to become the most preferred destination for innovation and technology-driven businesses.
Dubai also has plans to convert 25% of all vehicles to autonomous driverless AI-based vehicles by 2030 to realize enormous time savings and a huge rise in manpower productivity.
Dubai also plans to switch over to renewable energy with the help of innovative technologies and under its clean energy strategy wants to reduce the city’s dependency on conventional energies by 75% by 2050. The Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park in Dubai is the largest single-site solar park in the world that would have the capacity to produce 5,000 MW of power by 2030.
The country focuses on promoting global free trade agreements and agritech that would help it become the world’s number one country in the Global Food Security Index by 2051.
Final Thoughts
As Dubai UAE accelerates the pace of digital transformation and adoption of smart technologies, opportunities galore for Indian technology firms and professionals. India is the leading innovation hub in the world and has a vast IT talent pool. India and the UAE have been great partners on multiple fronts including IT.
There are multiple opportunities for Indian entrepreneurs who can leverage Dubai’s rapid digital transformation and set up companies with the help of reputed and professional business setup consultants in Dubai.

- NEWSLETTER,SINGAPORE
- January 9, 2023
The Fourth Industrial Revolution often known as Industry 4, combines the physical and digital aspects of manufacturing technologies and helps address many challenges of today’s manufacturing sector. Singapore, as the leading manufacturing hub in Southeast Asia, has already embraced Industry 4.0 to take this sector up its value chain to an advanced level.
Singapore has a well-developed manufacturing ecosystem and the country, with the help of a highly skilled talent pool and government support is all poised to embark upon this advanced technology-based manufacturing transition.
Thousands of global business organizations and MNCs have chosen Singapore as their regional headquarter for an effective transition to Industry 4.0 to optimize profit and sustainable business growth. This in turn has led to an increasing number of Singapore-based startups collaborating with these global business houses for future business innovation and excellence and boosting the startup ecosystem for attracting foreign investment in the country.
Smart Industry Readiness Index: Supporting the Manufacturers in Singapore
The Economic Development Board (EDB) of Singapore in association with leading technology companies and industry experts developed the Smart Industry Readiness Index (SIRI) to support the manufacturing companies in Southeast Asia in assessing their readiness for Industry 4.0. This tool, as developed, has four main focus areas including Data analytics, Connectivity, Advanced manufacturing technologies, and Workforce development.
This tool was first launched in 2017 to help the manufacturers identify the areas where they need to make changes to be ready for Industry 4.0 by carrying out the initial gap analysis of their current level of readiness in each of these four areas to start, scale, improve and sustain their manufacturing operations. SIRI also helps the manufacturers conceptualize Industry 4.0 and develop an innate understanding of the present Industry 4.0 maturity level of the companies by evaluating their organizations, processes, operations, and technologies including IoT, AI, Cloud computing, and Robotics.
Industry 4.0: Singapore’s Increased Focus Upon Research and Development
Today, over 20% of Singapore’s GDP is contributed by the manufacturing sector which is considered the building block of the country’s economy.
The country is a global leader in various manufacturing sectors including pharmaceutical and healthcare products, semiconductor manufacturing, and aerospace engineering, and has attracted many internationally reputed giant companies like GlaxoSmithKline, Siemens, Schneider Electric, IBM, Accenture, HSBC, Shell, UOB and many more to set up their manufacturing bases there.
The country’s relentless drive and increasing budgetary spending in manufacturing research and development (R&D) are promoting smart technologies adoption in the manufacturing sector and attracting global investors for new company setup in Singapore. The Singapore government has plans to spend around SGD 17.6 billion for R&D over the next five years in its continued effort to build sustainable and more resilient manufacturing industries in the country.
While 20% of the funds are budgeted for innovation platforms and entrepreneurial talent development and enhancing business innovation capabilities, the remaining 75% is allocated for new programs focused upon future needs, disruptive emerging opportunities, and talent and skill development in the manufacturing sector.
The universities and research centers in Singapore are building model factories and processes to simulate real-life manufacturing environments for the development of new manufacturing technologies that can be exported to different countries across the world.
Industry 4.0: Why Choose Singapore
The biggest challenges in implementing Industry 4.0 lie with finding qualified employees, obtaining continuous government support, and upgrading equipment and facilities and Singapore continually strives for addressing these challenges effectively.
Singapore boasts of a highly skilled workforce and is ranked second globally in the Global Talent Competitiveness Index, 2021. The country’s robust education policy and system help the students become more focused on smart technologies and attain greater proficiency in science, technology, and mathematics. Singapore has a talent pool of the best available technical and vocational skills for catering to the manufacturing sectors’ manpower demands with more than 30% possessing a university degree and another 15% holding field-specific professional qualifications.
Universities and research centers collaborate with leading MNCs to establish corporate laboratories and develop innovative and smart solutions to address real-life Industry 4.0 challenges including cybersecurity, computational engineering, AI, blockchain, artificial intelligence, and green production techniques.
Skills Future, a national program launched in 2015 supports citizens in honing their technical skills and provides technical training programs, online tutorials, and industrial internships offering financial benefits. This initiative, in particular, helps people make well-informed decisions in choosing training courses, fields of education, and professional careers matching their qualifications. This program also encourages lifelong learning, promotes employee recognition, and focuses on developing skills to adapt to innovative technologies most needed and vital for Industry 4.0.
Several support measures are taken by the government to promote Industry 4.0 and make the country more business friendly. The country offers several tax exemptions, easy transfer of ownership, and avoidance of double taxation. Various fiscal and non-fiscal incentives including a stable socio-political environment are also conducive to boosting Industry 4.0.
The country has a simple but robust business setup process which is free of bureaucracy and streamlined for an easy and fast Singapore company incorporation for foreign investors looking to establish a business base in the country.
Singapore company incorporation is a hassle-free process and usually takes a day if all the required documents are in order. Private limited companies are the most preferred choices among foreign investors being the most flexible, scalable, and advanced business vehicle.
The Takeaway
The manufacturing sector in Singapore is witnessing continuous technology and processes transformation including 3D printing, robotics, AI, and IoT. Companies that are embracing Industry 4.0 have started to reap great benefits in terms of productivity, efficiency, and bottom line.
Successful implementation of i3D printing technology is helping companies to do away with huge inventories and manufacturing products only on demand. Storage, manufacturing, and inventory carrying costs are greatly reduced making manufacturing companies more resilient and sustainable in the long term. Increased use of data, the essence of Industry 4.0, is helping companies to achieve increased operational efficiency and improved demand forecasting.
As manufacturing in Southeast Asia plays a vital role in the region’s economy, Industry 4.0 can hugely transform business operations and bring about significant economic growth.


- Article, U.A.E
- December 19, 2022
Taxpayers in the UAE should prepare for new VAT changes effective January 1, 2023. It is advisable to consult tax consultants in Dubai promptly due to the significant impact of the recent amendment on your business.
Key dates
- The revised, amended provisions became effective from January 1, 2023
- As per new rules, qualifying registrants must submit reports from July 1, 2023
- The FTA kindly requests Qualifying Registrants to inform them by March 15, 2023
FTA updates the UAE VAT’s Tax Policy and Executive Regulation. The Federal Tax Department has modified the essential regulations surrounding UAE VAT:
Federal Decree-Law No. 28 of 2022 Modifications, Part I (Tax Procedures)
II. Act No. 8 of 2017’s executive rule amendments (Executive Regulations)
Based on the interpretation of the precise wording of the pertinent legislation, we have offered a comprehensive understanding following table:
1. The Federal Decree-Law No. 28 of 2022 updates Federal Decree-Law No. 7 in 2017 of a UAE on VAT, which will take effect on March 1, 2023.
| Article | Title | Modification | IMC Remarks |
| 1 | Meaning | The terms “Tax Residency Certificates” and “Tax Residency” now have new terminology. A few small changes were also applied to the tax and business concept. | For the Corporate Income taxes of June 1, 2023, the changes above were done to the legislation to ensure compatibility. |
| 5 | Linguistic | In addition to Arabic, the Council can consider materials in other languages. In particular, if the Government demands it, an Arabic version could be necessary. | Corporate and personal coordination with the Tax Authority will be improved. |
| 7 | Legal Advocates | Members, too, can comply with any new obligations and present tax records to the Board. | If the taxpayer is a juvenile or incompetent, there are no restrictions on filing the tax return. |
| 10 | Voluntary Disclosure (VD) | When there is no increment of taxable income, individuals must file the VD. The segments and penalty provisions will be outlined in the Executive Order. | Taxpayers may not be able to rectify errors in the subsequent report. |
| 16 | Power to do an internal audit |
|
|
| 23 | Tax Evaluation |
|
Help taxpayers determine the appropriate income tax. |
| 24 | Penalty for Regulatory Evaluation | Administrative fines ranging from a set AED 500 penalty to a high equal to double the taxes | Reduced the burden on taxpayers |
| 25 | Tax Offenses and Sanctions |
|
It lessened the strain of covering the initial sum—someone who fully adheres to the legal system and supports the Authorities. |
| 32 | Submission of a complaint and any other non-acceptance instances | Within 40 business days, an appeal to the Council’s judgment must be filed. | Taxpayers are given more time to submit their complaints. |
| 36 | Jury’s appeal system processes | The panel’s judgment could be challenged within forty days. | Chance to challenge in courts within the given timeframe |
| 46 | Limited Time Period | Whenever five years have passed, the authority can impose tax assessments or perform tax audits in case:
|
It gives the Authorities more chance to execute tax evaluations within the given timeframe, appearing in judgment. |
In addition, the following additional sections are added for offenses involving taxes, reviews of valuations, complaints, and reviews.
| Article no. | Details |
| 26 | Measures and Techniques |
| 27 | Agreement on Tax Fraud Charges |
| 28 | Petition for a Taxation Modification |
| 29 | Increase in Timelines |
2. Cabinet Decision No.99 of 2022 revised Executive Regulation – Law No. 8 of 2017 and will prevail on January 1, 2023.
The concept of service has now been changed in Article 3, exempting services offered by an entity to carry out duties as a board of any private or Government organization.
Article 72, which deals with monitoring the contributions made, has already been modified to the following extent:
- Where a taxpayer has a business located in the UAE, no permanent premises must have detailed records
- When services provided by a taxpayer into an ECO surpass AED 100,000,000, they must maintain documents to demonstrate the Emirate wherein the supply is acquired
- The crossover threshold is also used to determine the provision’s relevance
Our Comments:
Since adjustments must be made to how enterprises are now operating, a modified federal decree-law, tax regulations, and administrative regulations are released. Therefore, organizations must ensure that the changes above are made to the relevant evidence and procedures as soon as possible before the law takes effect to prevent any legal implications.
How can IMC help?
IMC can assist your business by conducting a simulated audit that replicates the type of assessment the FTA may work. This audit will pinpoint any areas of non-compliance and provide recommendations to align your business with the UAE VAT regulations.

- Article, Global
- December 12, 2022
The COVID-19 pandemic and technical improvements throughout industries forced businesses to adopt remote working as an essential component of the fundamental corporate strategy. Even so, every firm performance in times of turmoil depends on its ability to transition towards this novel standard operating style.
Due to this change, businesses’ three most frequent difficulties are finding, recruiting, and keeping successful remote workers. Many service providers offer Global EOR Services for recruiting ideal remote employees.
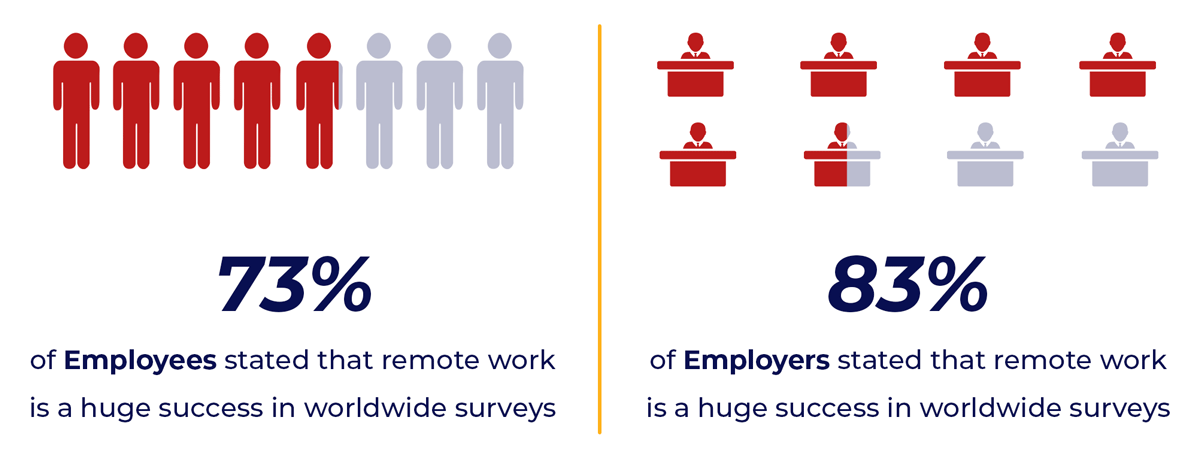
Employing workers remotely necessitates a more deliberate approach. Furthermore, 73% of employees and 83% of employers stated that remote work is a tremendous success in worldwide surveys. Not only are you attempting to connect the ideal individual with the right job, but you are also looking for people who would be comfortable working remotely. Let us explore more about this:
Remote working: An overview
Everything is evolving due to remote working, including our views on work-life balance, communication methods, and efficiency evaluation techniques. Several regulations that previously set the limits of our working lives have changed due to the “massive remote operational experiment.
The job market will undoubtedly entail decentralized, transnational, co-located, and remote skilled workers that use online tools to stay in contact efficiently. Several businesses have practically stated a WFH “permanent” plan, and according to 53% of American survey, participants will do at least some of the future projects from home.
Essential Points to Consider While Recruiting Remote Staff:
While it may be simple to hire remotely, it might be more challenging to switch to a workspace that values remote workers. Once you’re managing payment in several nations, attempting to interpret several employment rules, and managing taxation, geographical boundaries still play a significant role.
Finding world-class talent in the industry is among the significant issues businesses undertake. Despite millions of available jobs posted daily, the employment market is highly competitive. Let us consider some important aspects while managing remote working recruitment:
1. Payroll Management:
Despite the most straightforward situations, payroll might be a hassle, particularly for small enterprises with financial accounting. Managing payroll might be legally risky if you recruit people worldwide in new regions.
The logical move is to connect with Payroll outsourcing solutions for a sustainable administration of the employers of reference in case the company wants to build a branch overseas.
2. Probability of A Permanent Establishment
Organizations with a consistent presence in a nation are referred to as “permanent establishments” for accounting purposes. If the nation has a permanent establishment, corporate income taxes could be levied overseas. Companies may also adhere to regulatory requirements that differ from those of other foreign businesses.
3. Invention and IP Rights
Even traditional office structures allow for a country’s capital of workplaces at a time, creating intellectual property rights a little easier to understand. Global recruits make it a little more complicated.
There are times when remote workers do not use business property, tools, or expertise. Losing IP rights due to ignorance of international norms may lead to legal disputes, reputational harm, and other issues.
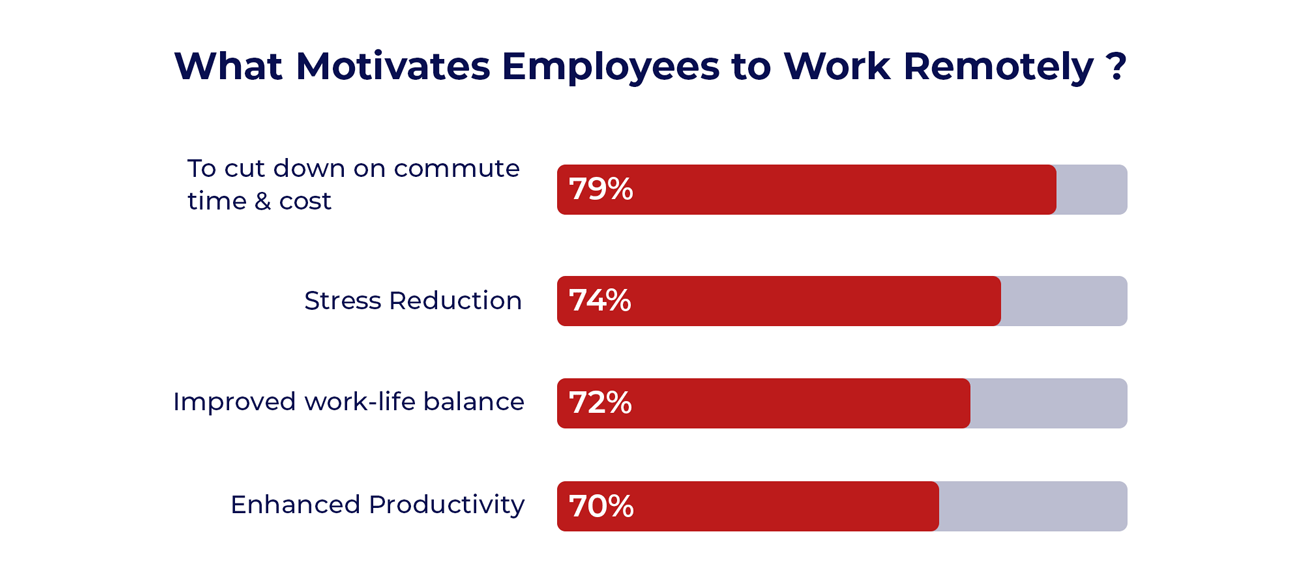
Advantages of Remote Working:
Global Employee Benefits Solutions manages the merits and drawbacks of remote work. Meanwhile, building diverse personnel was never more straightforward, thanks to software products that support routine activities and streamline communication.
The primary benefits of remote working for business units all centre on how it affects regular activities, profitability, and workforce well-being. Below are a few benefits of working remotely for the corporate project team:
Savings on Teamwork Activities
Interaction is Upgraded
Advanced Skilled Workforce
Improvements in Employee Wellbeing
Gains in Efficiency
Process of Remote Work Recruitment:
Develop a Job Specification
Examine Resumes and Choose the Ideal Candidate
Arrange the Teleconference Interview Schedule
Evaluate the Candidate's Competence
Examine the References
Develop an agreement
Conclusion:

A Member Firm of Andersen Global
- 175+ Countries
- 525+ Locations
- 17,500+ Professionals
- 2350+ Global Partners

















 IMC Group
IMC Group