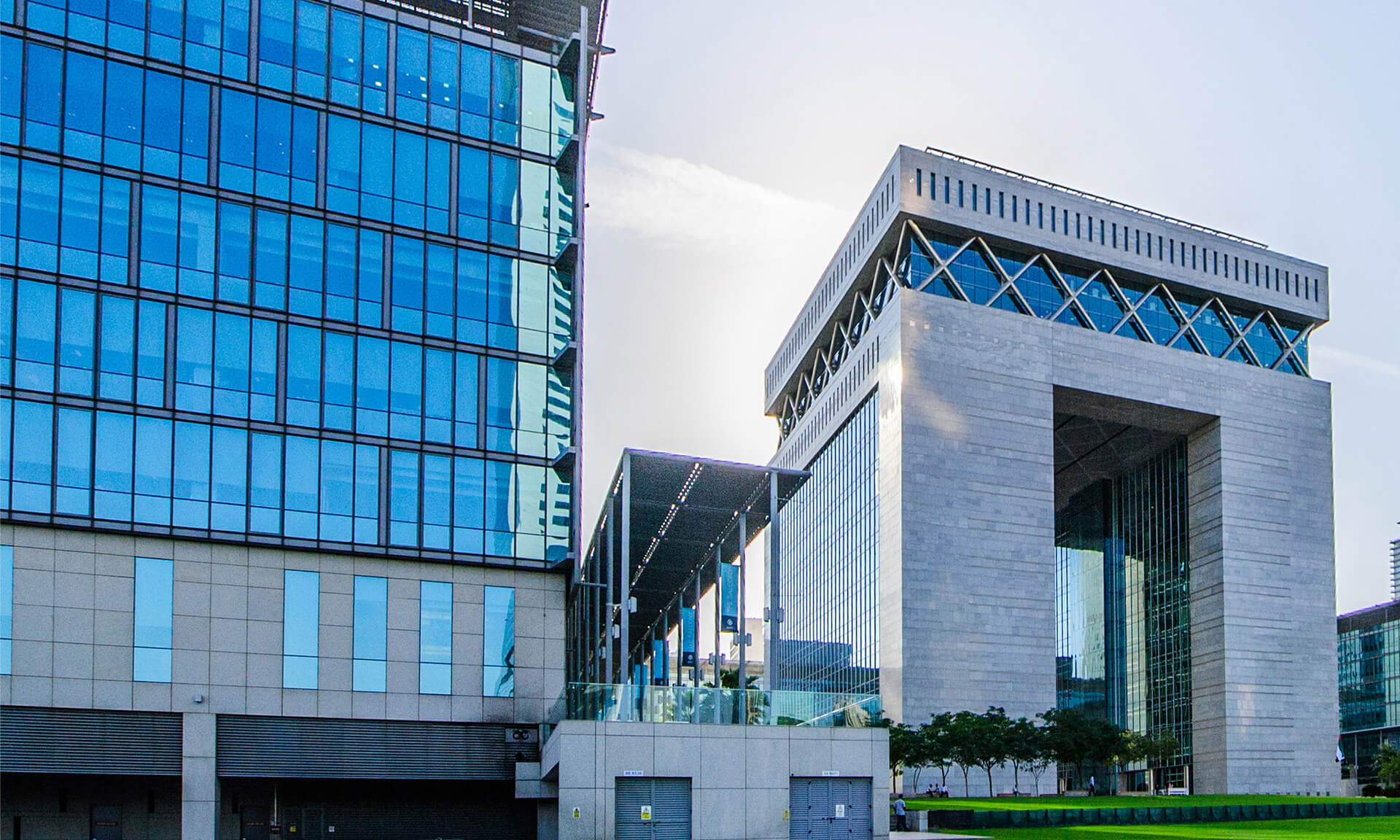

- Newsletter, U.A.E
- April 15, 2021
In March 2021, the WAIFC board unanimously agreed to recognize the DIFC, the leading financial center in the MEASA region as a member of the association, the 4th from the GCC to spearhead the development of digital finance and in the areas of Fintech, Sustainable Finance, and Innovation.
As a non-profit organization located in Brussels and founded in July 2018 in Paris, the WAIFC represents the top nineteen global financial centers across four continents that promote and share best practices in the field of finance with a varied scope of activities and benefit from the collective strength of its members. The alliance as city governments and other financial institutions also facilitates cooperation amongst the group members and interaction with the general public besides developing and promoting their financial Centres.
As a member of WAIFC, DIFC as the highest-ranked financial center in the MEASA region will now collaborate with other leading global financial centers in Tokyo, London, Paris, Frankfurt, Toronto, and in many other countries on global best practices some of which are already entered into memorandums of understanding with DIFC.
DIFC with the vision to drive the future of finance is focused on embracing new and innovative technologies in the field of finance and aims for achieving sustainable economic and social goals including Environmental protection.
“We are very pleased to have DIFC join our association. Dubai is a leading global financial center, and DIFC will undoubtedly bring a valued contribution to our initiatives. We are very much looking forward to working with the colleagues in Dubai,” remarked Jennifer Reynolds, the Chairwoman of the WAIFC.
CEO of DIFC Authority, Arif Amiri highlighted: “DIFC is pleased to be joining the World Alliance of International Financial Centres. The Centre is looking forward to representing Dubai and building partnerships with other members so we can be a collective force for good. Together we can make progress in areas such as FinTech, innovation, sustainable finance, and developing digital economies. We can align our approaches which will allow us to cohesively drive the future of finance.”
Dr. Jochen Biedermann, Managing Director of the WAIFC, added: “DIFC has been an observer to WAIFC since last year, and we are delighted that it will join WAIFC as a full member now. DIFC has had a phenomenal development in less than twenty years from its first steps to one of the world’s leading financial centers. We are very much looking forward to exchanging best practices and learning from each other.”
Sheikh Maktoum Bin Mohammed Bin Rashid Al Maktoum, Deputy Ruler of Dubai and President of DIFC with his able leadership taken DIFC to the pinnacle of its performance during 2020 amidst global economic uncertainty caused by the pandemic and elevated the country’s status as a pivotal global economic destination with many businesses reporting exponential growth, including capital markets, asset management, FinTech, professional services, and banking aided by a conducive FinTech and venture capital environments, cost-effective licensing and easy DIFC management startup license, flexible regulation, innovative promotional events, and easy access to funds for start-ups.

- Newsletter
- April 15, 2021
Of late, a multi-cloud strategy has become the leading option for business entities as the survey found an increase in usage of approximately 15 percent between 2019 and 2020 mostly fueled by covid 19 pandemics. Multi-cloud is composed of more than one cloud platform including public, private, and hybrid clouds. Independent of any single cloud platform, a multi-cloud platform offers increased flexibility, reduced cost, enhanced scalability, and many other advantages. There also remain some cons that need to be addressed before switching over to multi-cloud such as increased training needs of personnel, reduced interoperability between applications and services, non-availability of many skilled professionals, increased operational hiccups, logistical complications, etc. However, the benefits far outweigh the cons.
What are the Pros and Cons of a Multi-Cloud Platform?
A quick look into the benefits of multi-cloud platforms often justify its enhanced usage by business entities and the most common benefits are
- Continuous Availability with little or no possibility of a service break down if one cloud goes down a business can be functional on other deployed clouds
- Flexibility and freedom of choice of platforms and solutions best suitable for your business needs
- Empowering customers to negotiate on price with ample visibility on cost and benefits
- Faster speed and better network performance with service providers having data centers closer to your locations
- Improved scalability based on business demands and extent of usage
- Quick innovation due to increased access to a wide range of tools and choosing clouds providing the best sets of services
- Better prevention of DDoS attacks as data is stored on different platforms
- Mitigating shadow IT as individual departments have accessibility to solutions as per their needs and without any need to bypass IT department
Though investing in a Multi-Cloud solution is usually a smart and beneficial investment strategy, it also comes with its fair share of challenges as
- Increased management complexities arising out of vendor-specific monitoring consoles and cloud architectures
- Increased remuneration and short supply of skilled professionals including architects, developers and testers and, administrators
- Multiple factors influencing billing and pricing for increased issues with cost analysis and reporting
- Security issues as a multi-cloud environment are more difficult to secure with several aspects to consider including encryption key, SS/TLS encryption, secrecy management, access controls, etc.
- Compliance issues as vendors can have non-standard models
- Complexities in the integration of individual SaaS solutions and reduced interoperability
What are the benefits of Cloud Accounting?
As flexibility is the essence of today’s business, we should be able to manage business operations independently of a central setting. Cloud Accounting and Bookkeeping Services offer us this advantage with several other benefits as mentioned below
- Ease of accessibility from anywhere and anytime
- Automated accounting tasks
- Real-time accounting data with better accuracy
- Ability to coordinate and collaborate even when physically distanced
- Improved data security
Strong platform features are indispensable while you choose a remote accounting platform and must-have functions that can enable you to communicate, update and share accounting data, secure information, and manage operations.
Cloud accounting platform Zoho is equipped with tools that enable remote working with several additional features and Zoho Implementation partners can identify, customize, integrate and implement the right set of Zoho tools to effectively address every business needs.
What are Multi-Cloud Models?
Multiple clouds provide strategic services to meet specific business and technical needs and are primarily classed as Software-as-a-service, or SaaS, Infrastructure-as-a-service, or IaaS and Platform-as-a-service, or PaaS.
There are many players in the multi-cloud market segment and deployments can either be a blend of public plus public or public plus private clouds. There can be different models based on business functions running on different platforms such as production running on on-premise infrastructure and development running on a public cloud. In a separate model, a single business function can run simultaneously on a multi-cloud.
What is the Future Outlook of Multi-Cloud Systems?
Multi-cloud environments are going to stay and flourish with time due to cost optimization, operational ease, and increased effectiveness. Cost optimization tools are also coming to the market for analyzing processes to maximize cost savings.
As per global surveys and market research in 2021, the multi-cloud management market is all set to expand at a CAGR of more than 25 percent between 2020 and 2026.

- Article, U.A.E
- April 13, 2021
Are you an ambitious entrepreneur or a forward-thinking business planning to set up a business in Dubai? This is one of the most dynamic cities in the United Arab Emirates that attract investors from all around the world. Commercial opportunities in the UAE are lucrative indeed, and with globalization, international businesses are keen to make the most of these profitable opportunities. As per the 2024 World Competitiveness Report, Dubai ranked 7th globally in terms of business efficiency.
Dubai has a cosmopolitan population. It is the home to approximately, 7.8 million immigrants, compared to 1.4 million Emiratis.
In this comprehensive blog, we have presented a step-by-step guide on how to register a company in Dubai from India. As an Indian resident, creating a company in Dubai can be overwhelming unless you are aware of the stringent incorporation laws in the country. Don’t worry, as we have holistically discussed the steps for company registration in Dubai.
- 10 Key Benefits of Company Registration in Dubai
- Documents checklist for company registration in Dubai for Indian nationals
- What is the minimum investment required to start a business in Dubai?
- Company Registration in Dubai: Different Types Of Businesses
- Different Types of Business Licenses for Company Registration in Dubai
- How to Incorporate a Company in Dubai from India online: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Key Sectors Driving Dubai's Economic Growth in 2024
- Things to Do After Creating A Company In Dubai
- Consult IMC Group for Creating a Company in Dubai
10 Key Benefits of Company Registration in Dubai
- Strategic demographic location: Dubai is strategically located at the crossroads of Asia, Europe, and Africa. Providing an easy access to the international market, it is ideal for businesses looking to expand globally.
- Superior infrastructure: For global trade, Dubai is a prime location as it offers a world-class infrastructure. From transportation to business facilities, it is an ideal gateway to international markets.
- Streamlined business setup: The complete process for registering a company in Dubai as a foreigner is straightforward and takes little time. The country offers more than 2,000 business activities to choose from.
- Tax benefits: One of the prime benefits of registering your business in Dubai is the favorable tax regime in the country. Consider the exemption of corporate and income taxes, hidden fees, and import and export duties in the country. This transparency in Dubai makes its environment business-friendly. In Dubai, the standard VAT rate of 5% is among the lowest in the world. Low tax rates allow Indian companies save money on taxes and allocate them on core business priorities.
- Specialized Free Zones: In Dubai, foreign companies can operate in specialized free zones that cater to specific industries. These Free Zones have their own legal framework and has streamlined their regulations. This empowers foreign businesses to operate more flexibly.
- 100% foreign ownership: When you set up business in Dubai as a foreign individual, you can benefit from complete control through 100% ownership of the registered company.
- Agile and cost-effective workforce: The labor laws in Dubai provide an ideal framework to attract talent and retain staff. This empowers Indian entrepreneurs build a competitive workforce in the country.
- Security of investors: In Dubai, laws upheld by the DLD, RERA, and DED are impartial and supportive to foreign investors. The crime rate in the city is 0%, which makes it a haven for Indian companies interested in creating a company in Dubai.
- Growth in population: In Dubai, the population is expanding and its economy is rapidly evolving. This is a popular location for startups. Also, foreign investors choose Dubai as a base for expanding their companies. The growing population in Dubai ensures that they get customers in the long run.
- Seamless visa management: If you are wondering how to register a company in Dubai from India as you need to deal with the visa of your employees, the process can be amazingly ease. Reputed professionals at IMC Group provide comprehensive global mobility services. Along with your business license, they can also help you process the visa.
During Q1 2024, the Dubai Chamber issued 191,013 certificates of origin, which is a 7% increase compared to the previous year.
Documents checklist for company registration in Dubai for Indian nationals
- Receipt of Initial Approval
- Copy of Lease Contract (Attested)
- Memorandum/s of Association
- Copies of Submitted Documents
- Government Approvals (if applicable)
- Business Plan
- Completed Application Form
- Existing Trade License/Certificate (if applicable)
- Manager Registry Identification Code (RIC) Form (Original & Notarized)
- Shareholder & Manager Passports
- Specimen Signatures of shareholders and appointed manager
- Letter of Intent
- Financial Documents (as required)
- Title Deeds (if applicable)
What is the minimum investment required to start a business in Dubai?
Company Registration in Dubai: Different Types Of Businesses
Types of Business Setup in Dubai
Dubai Mainland Company Registration
- Mainland companies in the country are integrated within the legal framework of the UAE. These companies need to adhere to the regulatory standards of the country and follow the national corporate taxation policies.
- Dubai Mainland Companies can freely carry out their business activities across the UAE. They can also own or lease properties in the mainland areas.
- Such type of business setup is ideal for companies planning to integrate them deep in the local market. These businesses offer products or services directly to the customer base in the UAE.
- Operating in the mainland facilitates broader activities and business engagements. These include government contracts and access to a more extensive market within the UAE.
FY 2022-23: Trade between India and the UAE reached $84.5 billion, a 16% increase from $72.9 billion in FY 2021-22
Dubai Free Zone Company Registration
- During company registration in Dubai, Indian businesses can choose a free zone company in the city. This allows them to capitalize on benefits like corporate tax exemption and specific regulations applicable on mainland companies. This creates a significantly favorable business environment.
- Free Zone companies in Dubai can operate only in the designated zones. The city has tailored areas for each business category.
- Usually, Free zone companies in Dubai cannot own mainland properties. However, you can take advantage of 100% foreign ownership and retention of profits.
- If you are focussing on a specific sector, it’s logical to set up business in Dubai Free Zones. Companies requiring a strategic base for exports or re-exports can benefit from the tax-efficiency in Free Zones.
- Dubai Multi Commodities Center (DMCC)
- Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA)
- Dubai Design District (D3)
- Dubai South/Dubai World Central (DWC)
- Dubai International Financial Center (DIFC)
- Dubai Silicon Oasis Authority (DSOA)
- Dubai Technology Entrepreneur Campus (DTEC)
- Dubai Airport Free Zone Authority (DAFZA)
Dubai Offshore Company Registration
- In Dubai, offshore companies offer an attractive prospect for businesses carrying out international trade while prioritizing their asset protection. These companies don’t have the obligation to comply with specific regulations related to local corporate taxes.
- If you are planning to set up business in Dubai to operate beyond the borders of the UAE, offshore company registration will be the right choice. This type of business setup offers confidentiality and privacy, while you can efficiently plan international taxation.
- Offshore business registrations are suitable for holding companies carrying out investment activities or international trading. It offers both financial security and efficiency.
Different Types of Business Licenses for Company Registration in Dubai
- Trade license: Businesses engaged in trading activities in Dubai, like selling or buying goods, need a trade license.
- Industrial license: A trade license is applicable to companies that produce or fabricate goods, or are engaged in manufacturing or industrial activities.
- Professional license: Those engaged in service-oriented businesses in Dubai based on their skills or expertise, like artisan, professionals, and craftsman, should get a professional license.
More than 15,000 new Indian companies registered in Dubai during FY 2022-23, reflecting a growing interest in business opportunities
How to Incorporate a Company in Dubai from India online: A Step-by-Step Guide
Define your commercial activity
- Commercial trade
- Industrial
- Consultancy services
- Educational
- Ecommerce
- Offshore operations
- Media
- Freelancing
- Manufacturing
- Warehousing
Choose the right business structure
Free Zone Companies
| Type of Company | Key Features | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Free Zone Limited Liability Company (FZ LLC) | Offers limited liability to shareholders, allows multiple owners, whether individuals or corporate entities | Businesses with multiple shareholders (individuals or corporate) |
| Free Zone Company (FZ Co.) | Similar to FZ LLC but subject to specific free zone regulations | Businesses in specific free zones |
| Free Zone Establishment (FZE) | Offers limited liability but for sole shareholders | Single-owner businesses |
Mainland Companies
| Type of Company | Key Features | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Liability Company (LLC) | Provides limited liability, allows a wide range of business activities | A popular choice for general business activities on the mainland |
| Sole Proprietorship | Complete control for individual entrepreneurs but with personal liability for business debts | Entrepreneurs preferring full control but accepting full liability |
| Civil Company | Suitable for professional services like consulting, law, or accounting | Professional partnerships (consulting, law, etc.) |
| Branch or Representative Office | Allows foreign companies to set up for marketing and business activities with regulatory constraints | Foreign companies looking to establish a presence in Dubai |
| Type of Company | Key Features | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Partnership Company | Collaborative structure for two or more partners, sharing management and responsibilities | Businesses with shared ownership and management |
| Public Joint Stock Company (PJSC) | Designed for large ventures with the option of public share offerings and strict regulatory adherence | Large enterprises seeking public investment |
| Private Joint Stock Company (PrJSC) | Similar to PJSC, but for private share distribution; ideal for sizable private ventures | Large private ventures |
Offshore Companies
| Type of Company | Key Features | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Offshore Foundation | Non-shareholder entity used by non-profits or for asset management | Non-profits, asset management entities |
| Offshore Trust | Focuses on asset protection and beneficiary planning | Asset protection and privacy-focused businesses |
| Limited Liability Company (Offshore LLC) | Offers limited liability, generally exempt from local taxes, ideal for international businesses without physical presence in Dubai | International businesses without physical presence |
| International Business Company (IBC) | Exempt from local taxes and duties, suitable for international operations such as trading, investment, or holding company | International trading, investment, or holding companies |
Approximately 30% of the UAE's population (around 3.5 million) are Indians, fostering strong cultural and business ties
Register the Name of Your Business
Choose a name for your company as you set up business in Dubai. Check the availability of this name with the relevant Free Zone Authority or Dubai Economic Department (DED) to make sure it has not already been taken. Here are some guidelines to choose the ideal name for your business in Dubai.
- Include the legal form abbreviation (LLC or FZ LLC).
- Avoid offensive or inappropriate terms.
- Ensure the name aligns with your business activities.
- Do not use government names, logos, or symbols.
- Choose a unique, unregistered name.
- Obtain approval from the Department of Economic Development and Ministry of Economy.
Decide the Location
While creating a company in Dubai, you need to lease or rent a commercial space based on the needs of your organisation. Choose the mainland or a Free Zone following which you need to sign a Tenancy Contract, which typically remains valid for one year. Businesses must also obtain an Ejari Certificate and submit it to the issuing authority. The final license must include the address mentioned in your Tenancy Contract.
Additional documents may be required based on the type of premise you select. It can be an office in a commercial complex, a flexi-desk office, a standalone office, a retail space, or a warehouse.
Apply for Your Business License
- Initial Approval: During the initial approval, the authorities confirm your business name, structure, and its activities.
- Verifying documents: The authority will schedule a meeting to verify your documents like passports of shareholders or UBOs (Ultimate Beneficial Owners). Next, key documents like the Board Resolutions, Articles of Association (AOA), and Specimen Signature Forms need to be signed.
- Obtain the Business License: Next, businesses can receive the necessary approvals and fulfill their payment obligations. The authorities will then issue relevant corporate documents, including the business license. Businesses involved in sectors like healthcare, travel, and tourism may need additional approvals from specific departments of the government.
Key Sectors Driving Dubai's Economic Growth in 2024
| Key Sectors | Growth Rate | Contribution in GDP | Contribution in GDP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation and Storage | 5.6% | AED 15.4 billion | This sector was one of the top performers, largely driven by increased air transport activity. |
| Financial and Insurance Activities | 5.6% | AED 15.1 billion | Strong performance in credit and deposit balances supported this growth. |
| Information and Communications | 3.9% | AED 5.1 billion | Continued advancements in technology and communication services bolstered this sector. |
| Accommodation and Food Services | 3.8% | AED 4.7 billion | High hotel occupancy rates, averaging 83%, fueled growth in tourism-related services. |
| Real Estate | 3.7% | AED 8.4 billion | The sector benefited from a notable increase in real estate sales, up by 22%. |
| Trade | 3% | AED 26.3 billion | The wholesale and retail trade sector remained a major contributor to GDP, representing approximately 22.9% of the total economy. |
Things to Do After Creating A Company In Dubai
After obtaining your business license, consult experts for further assistance. This includes:
- Arranging visas for employees and investors
- Acquiring Emirates ID
- Opening a bank account
- Setting up your accounting or bookkeeping system
Consult IMC Group for Creating a Company in Dubai
Ready to set up your business in Dubai? Don’t let the stringent norms and legal complexities derail your ambitious plans. With expert guidance from professionals, you can simplify the process of creating a company in Dubai. The IMC Group continues to be your trusted partner, offering holistic assistance for company registration in Dubai. From obtaining your trade license to registering your company and opening a bank account to arranging visas, these experts have you covered. The professionals also streamline operations with outsourced accounting and bookkeeping services. Entrust professionals on these crucial aspects and focus on growing your business, which matters the most.
Contact the IMC Group today to get personalized assistance regarding your company registration in Dubai.

- Newsletter, Saudi Arabia
- March 31, 2021
A draft resolution detailing the technical and functional implementation guidelines of E-invoicing has been released on 18th March 2021 by Saudi Arabia’s General Authority of Zakat and Tax (GAZT) as an addendum of earlier released regulations published during December last year.
The E-invoicing implementation has been planned in two phases, the first one going live on 4th December 2021 followed by the second phase that would go live on 1st June 2022 GAZT has also announced that all businesses may not be needed to comply with the requirements by 1st June 2022 and the details will be published as a separate resolution afterward.
Unlike a handwritten or scanned invoice, an electronic invoice is generated, stored, and amended in a structured electronic format through an electronic solution that includes all the requirements of a tax invoice. Credit and Debit Notes issued in an Electronic format, as a result of amendments conducted in the Electronic Invoice are called electronic notes and don’t include photocopied or scanned paper notes.
E-invoicing will be used for VAT purposes and will apply to all taxable persons excepting the non-resident taxable persons and any other party issuing tax invoices on behalf of a supplier subject to VAT. Exempt supplies and imports of goods and services subject to Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) are excluded from E-invoicing requirements
The contents of an electronic invoice will have all Terms, requirements, and conditions applicable to tax invoices as per Article (53) of the VAT Implementing Regulation. All applicable provisions of tax invoices will apply to Electronic Invoices, including the rules of storage of tax invoices stipulated in the VAT legislation, and specifically, Article (66) of the VAT Implementing Regulation.
For simplified e-invoices and notes, a Quick Response (QR) code of a Base64 format with up to 500 characters must be generated and printed on simplified e-invoices and E-notes. Additionally, controls/mechanisms should be implemented to avoid tampering of the e-invoices.
The e-invoice and E-notes must be issued in XML or PDF format and shall generate a universally unique identifier. For simplified e-invoices and E-notes, businesses will need a cryptographic stamp to be included on the electronic invoices or notes.
The details regarding implementation timelines, targeted groups, and specifications for generation, storage and integration including approved external provider details for E-invoice Generation Solutions will be issued by the GAZT at a later date.
The implementation of Electronic Invoicing will have two phases and will include two specifications
- Phase one is for the generation and keeping of tax invoices and electronic notes in a structured electronic format issued through an electronic solution that combines all the requirements of tax invoices.
- Phase two is the Integration of the electronic solution of taxable persons used for generating electronic invoices and notes with the system of GAZT for data sharing.
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has planned to introduce e-invoicing as a step towards global best practices aiming for increased compliance with tax obligations, better consumer protection, and fair business competition.
As E- invoicing is made mandatory, businesses that need to issue E-invoices and/or E-notes as per E-invoicing Regulations must make themselves aware of necessary requirements.
All businesses must carry out an initial gap analysis for evaluating if their existing system and technical specifications of E-invoicing complies with the draft resolution requirements.
GAZT also welcomed public comments that can be shared till 17 April 2021 allowing taxpayers and E-invoicing service providers including advisors and other interested parties to comment on the draft resolution.

- Article, Singapore
- March 30, 2021
Are you striving to look for a legal way of how to remove a director in Singapore? Or you are tired of covering the poor performance of your company’s director, and you are looking for a legal way to terminate him? Well, there is no need for you to worry about this legal issue anymore. We are here to guide you all about the standard procedures and requirements of removing a director in Singapore.
A director is a crucial functional person of a company. All companies in Singapore must have at least 1 local director who must be Singapore Citizen or Permanent Resident and there is no maximum limit on directorship however one must check its company’s constitution for any restriction on maximum number of director.
As per the law of the land, a business can execute the removal of a director in Singapore in three ways, and they are as follows:
- Resignation
- Termination
- Disqualification
1. Resignation of A Director
The other legal manner of removing a director is when a director submits his resignation by himself. In case a director voluntarily submits his resignation from the directorship, then it can be deemed valid in the following conditions:
- If the resignation procedure is reasonable and is by the constitution of the company.
- The company shall have another director residing in Singapore.
Required Procedure of Resignation on the Part of Company
When the company receives the resignation of a director who voluntarily wants to resign from the directorship or if the director is deemed as disqualified, then in both such conditions, the company shall file a notification of cessation.
This procedure must be followed for 14 days only from the date of such change. i.e., the date of disqualification or the date of resignation. For submitting the notification with ACRA shall be accompanied and prepared with some relevant documents. Such documents are as follows:
- In the cast of disqualification of a director, a bankruptcy statement or a lawful court order must be accompanied when is applicable.
- In the case of voluntary resignation from directorship, the director’s resignation and the acknowledgment of the board of directors must be accompanied.
The former director shall notify the ACRA voluntarily in the following cases:
- When the former director believes that the company might not inform the ACRA regarding his disqualification or resignation.
- The former director knows that no other officers are competent or are in the company to notify the ACRA regarding his disqualification or resignation.
Failure to Comply with Procedure
In case the company and the former director fails to notify the ACRA regarding the company’s changes. Such non-compliance of the disclosure can be deemed an offense under section 165 of the Company Act.
As per Section 165 of the Company Act, the director or the chief executive officer may incur a personal liability and pay a fine amounting to $15,000 or liable for imprisonment up to 3 years. Unless the notification of cessation is submitted and is updated, the cessation shall not occur, and the former director will still be liable and responsible for managing the company’s affairs. In case the offense of non-disclosure is a continuing offense. The director or chief executive officer shall be liable for a fine amount to $1,000 for every day if the violation continues after conviction.
2. Termination of a Director
An individual working as a director can also be terminated but only based on a lawful and valid reason.
Termination of a Director on What Basis
The termination of a director can be made on various grounds such as:
- A company can terminate a director from his crucial position for his poor performance over significant months.
- Moreover, a director can also be released from the breach or non-compliance of his duties.
- A director can also be directly removed or terminated if he has been involved in any corporate scandal or
- Due to his poor management skills or leading skills, that are leading to low corporate performance.
Who has the Power to Terminate
The law of the land specifies the legal procedure to remove a director in Singapore. As per the law, the lawful process of removing a director is defined in section 158 of the companies Act. As per Section – 158 subsections, 8 of the companies act, a director in a company can only be terminated or removed by shareholders only.
The Procedure Of Removing A Director
In a Private Company
The basic rule of the land states that everything must be by the law of the land. The company needs to remove the director through lawful procedures only and according to its constitution. As per section 152 subsection 9 of the company act, only the company’s shareholders can remove or terminate a company’s director through a lawful and valid vote.
The director’s removal is a fundamental matter of the company, so the case goes to the board, and in a meeting, all the shareholders decide to vote for or against the motion. In the forum, at least 50% of votes are required to terminate or remove the director.
Moreover, for the requirement of a lawful removal of directors in Singapore, the shareholders have to give a written notice for 14 days. However, this requirement can also be waived off by putting it to the vote if more than 95% of voters favor not giving the 14 day’s notice.
As per the company’s constitution, a requirement of special resolution is specified, and more than 75% of votes are necessary for the removal of a director in favor of the motion. However, if the company has adopted the model constitution, then such a company can initiate the director’s removal through an ordinary resolution with accompanying 14 days of notice. If your company has adopted the Model Constitution in total, a director may be removed by standard resolution with at least 14 days of notice. However, as the initial process, all the company shareholders have to convene a general meeting to discuss whether they want to remove the company’s director and vote upon it.
If the shareholders decide to go for the director’s removal, they have to convene another meeting to pass the resolution. Moreover, on the other hand, the company’s constitution may also decide upon a clause to be included regarding the director’s termination in some specific situations. For instance, if a director does some immoral conduct or has a terminal disease. In such cases, the company will not be required to convene a meeting to pass a special resolution to remove the director. In case it is specifically required by the company’s constitution, then it is a necessity.
In a Public Company
The lawful procedure of removing a director from a public company is specified in Section 152 of the Company Act. Section 152 of the company act states the following requirement for making a lawful termination. The requirement of a legal procedure is as follows:
- A public company’s shareholders can remove a director by convening a meeting and passing an ordinary resolution. Moreover, for giving the resolution, at least more than 50% of votes must be in favor of removing the director.
- As per the legal procedure laid down in the company act, the shareholders shall convene a general meeting to start the process of terminating a director and must give special notice at least 28 days before the public forum; however, if it is not practicable, then at least 14 days before the date of convening the meeting.
When is a Director Officially Removed?
As per Section 152 sub-section 1 of the Company Act, the director’s termination shall not come to effect unless the company appoints a successor director to replace the former director. The removal of a director takes place and is made official only after the particulars of a new director have been updated in Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority.
3. Disqualification of a Director
In case of disqualification of a director, he shall not be allowed to manage any company’s affairs. The restriction of participating as a director shall remain unless the director takes permission from the General Division of the High Court or Official Assignee.
Disqualification of a Director on What Basis
The director can be disqualified from the company for numerous reasons, and they are as follows:
- In case the director announces that he is bankrupt.
- In case the court gives the order of disqualification of the director. For instance, an unfit director of an insolvent company or if a company is winding up due to national security or the director has been charged with offenses in Singapore.
- In case the director is convicted for the offense of fraud or dishonesty.
- If the director has been charged with offenses of three or more filing offenses under the Company Act within the last five years.
- In case the director has three or more of is companies struck off from the register by ACRA in the period of last five years
- In case the director has three or more orders from the General Division of the High Court against him for compelling or obstructing the inspection of the company’s registers, minutes books, or documents under section 399 of the Company Act or the provision to make returns under section 13 of the Act.
Term of Disqualification Period
The disqualification tenure of the director entirely relies on the reason for his disqualification. However, the general tenure of the director’s disqualification is five years.
What Does the End of Disqualification Period Mean for a Former Director?
Once the disqualification tenure of a former director is completed, a person may be appointed as a director of his former company or a new company. When the re-appointment of a former disqualified director is made, the company shall notify the ACRA of the appointment within 14 days from such appointment.

- Newsletter, Oman
- March 22, 2021
On 14th March 2021, the much-awaited Executive Regulations of Value Added Tax (VAT) was issued by the Head of Oman Tax Authority (OTA), His Excellency Saud bin Nasser Al Shukaili vide Ministerial Decision 53/2021. Oman’s Official Gazette no. 1383 published the regulations with guidelines for implementation. The VAT system in Oman will come into force on 6th April 2021 and the Sultanate is going to join the other three GCC member states viz the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Bahrain to introduce the levy.
VAT is being introduced in Oman keeping in perspective of the county’s ‘Oman Vision 2040’ initiative that stipulates the roadmap to diversify the oil-based economy to non-oil sectors including logistics, manufacturing, and tourism.
Online Registration for VAT
Only those holding a “commercial registration number” (CRN) can register for VAT through the online portal of OTA. The necessary forms and guidelines for registration were provided after OTA decided to implement a staggered registration schedule for those requiring VAT registration.
The schedule is staggered based on the income and businesses with an annual turnover of more than OMR 1 million can apply for VAT registration till the time it goes live. The upcoming registration schedule for income exceeding OMR 500,000 is likely to commence on 1st April and last till 31st May 2021.
Important Highlights of VAT Executive Regulations
The Executive Regulations provide ample clarity on most of the significant areas that were debated, discussed, and exhaustively studied over a long period considering social and economic impacts and clarify the applicability, rules, and procedures of the VAT Law including supplies, supply provisions, administrative matters, and penalties, tax points during transactions, VAT for online services, value assessment of supplies, exemption, and tax adjustments, totally exempted supplies, applicability in special economic zones, customs duty waiver, registration, de-registration, requirements of documentation, tax filing and invoicing, VAT returns, etc.
It is important for businesses to clearly understand the regulations that provide guidelines on the scope and extent of VAT exemptions and zero-rating. Businesses operating in areas that are exempted or zero-rated must be aware of the proper scope and applicability of such exemptions and zero-rating for their business activities and benefit from it.
Companies qualifying for VAT must also know other aspects of how VAT will affect their businesses and accordingly formulate appropriate plans and strategies for VAT compliance from the very first day. Some of the vital regulations are listed below:
Scope and Applicability of VAT
1. VAT Exempt Categories
The Sultanate of Oman has planned to levy VAT at the standard rate of 5 percent on most goods and services. The country, however, has announced some exceptions for essential food items, medical care, education, and financial services which will be exempt from VAT. According to OTA some 94 food items have been kept away from the VAT list including milk, meat, fish, poultry, fresh eggs, vegetables and fruits, coffee and tea, olive oil, sugar, nutritional products for children, bread, bottled drinking water, and salt to name a few.
2. VAT-Zero-Rated Categories
A zero-rated good doesn’t attract VAT owing to its social importance as a necessity. The sale of zero-rated goods is not taxed and credits are given on VAT paid on inputs. Any company engaged in dealing in zero-rated supplies is not included in the mandatory requirement of VAT registration.
Zero-rate or no VAT is imposed in Oman on essential commodities such as education and healthcare.
Businesses related to oil and gas; certain food items; cargo and passengers in global trade, some precious metals like gold, platinum, and silver; some life-saving medicines, medical equipment, and import and export of items can qualify for zero-rated VAT in Oman.
3.VAT-Other Categories
Besides the VAT exempt and zero-rated categories, some other categories classed as essential services also enjoy VAT exemption including financial services, reselling and renting of residential buildings, healthcare services and related goods and services, educational services, local passenger transportation services, import of goods to countries where there is no VAT and any return of imported items, goods, and services for military forces, supplies for no profit and charitable organizations, etc.
Commodities given free of charge such as any sample for business promotions will only attract VAT if the value exceeds either OMR 50 per person or OMR 1,000 in a year collectively and beyond these values, the commodities will be treated as deemed supplies and VAT will be levied on those.
Pre-Registration Input Claim of VAT
Per Executive Regulation Article 73, any input tax incurred before the registration can be claimed within 3 years maximum and article 74 says that the input tax incurred before registration for supplies of services can be claimed within 6 months maximum.
OTA must be informed within 30 days of registration for submitting a claim. For a tax claim valuing more than OMR 50,000 for goods stored as stocks, the audited stock list must be submitted to OTA for a claim.
Compliance of VAT
The Executive Regulations are mandated by the Omani Government stipulating certain compliance requirements which need to be compulsorily adhered to by an individual or company qualifying for VAT as per the regulations. Not complying with the stated compliance requirements may attract penalties as specified under the Executive Regulations.
Tax Invoicing of VAT
The executive regulations mandate the preparation and issuance of proper tax invoices for every single taxable supply including a deemed supply and against receipt of advance. The tax invoice should have all information prescribed by the OTA such as serial no, date of supply and receipt of payments, description and quantity of goods, details of customers and sellers, etc.
There is also a provision for a simplified tax invoice with less information than that in a complete tax invoice and is subject to prior conditional approval of the OTA that is usually received within 15 days from the date of application. A simplified Tax Invoice Format is mentioned in article 147 of the Executive Regulation with mandatory inclusion of the phrase “Simplified Tax Invoice” on it.
Tax Period and Return Filing of VAT
The taxpayers will need to file their returns every quarter starting from 1st January to 31st December of any calendar year. The VAT returns need to be filed online through a government portal and in the format specified by the OTA. The tax return along with the payment of the VAT must be done within 30 days from the end of a specific quarter.
Claim and Refund of VAT
The Executive Regulations demand all VAT claims to be submitted in a prescribed claim application format designed by OTA with specific information of VAT refund claimed, the reason for the refund including the tax period for which the VAT claim applies. All claims of refund must be submitted to the area authority within a maximum of five years from the end of the tax period for which it is due.
The VAT return can be claimed under the following conditions.
- If an extra VAT amount is paid then the due amount
- If VAT is paid by a non-resident of Oman
- If the VAT is paid by a foreign government or military or diplomatic officials
- If VAT is paid by foreign travelers while purchasing personal goods in Oman and not in commercial quantity and for carrying with them
- Refunds arising out of changes in the regulations and as announced by the OTA through Executive decisions from time to time
Services under the Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) of VAT
As per article 151 of Executive Regulation concerning imported goods or services, the taxpayer is responsible for recording the RCM. Unlike forward charging, a Tax invoice must be issued to self with RCM VAT in his favor if the supplier is a foreign resident and not registered with the OTA for paying the VAT.
Maintaining Records of VAT
The Executive Regulations specify the records to be maintained by the taxpayers including but not limited to the following.
- Details of day to day transactions in chronological order.
- Details of Inventory with inventory levels, items name, and types on a regular periodic basis.
- Details of supplies of imported and exported goods and services.
- Details of supplies of goods and services from GCC countries.
- Details of all Customs related transactions.
- All tax invoices including supporting documents issued by the taxpayers.
- All tax invoices and supporting documents received by the taxpayers.
- Records of information for validation of appropriateness of individual tax treatment.
Appeals for Tax Treatment of VAT
The Executive Regulations describe the method for putting an appeal before the OTA and in connection with the tax assessment or adjustment or any decision for VAT registration by the OTA. All appeals to the OTA need to be submitted in the Arabic language.
Penalties for Non-Compliance of VAT Regulations
Penalties amounting to OMR 500 to 5,000 are imposed for certain non-compliance such as
- Delay in submitting compulsory VAT returns
- The VAT registration certificate is not displayed properly and not visible to everybody
- Record keeping, accounting records and books, and necessary documentation are not maintained as per the specified requirements.
Some non-compliance can attract higher penalties and maybe as high as OMR 10,000 which are
- Inappropriate refund claims not supported by authentic records and documents.
- Non-submission of registration cancellation request when compulsory by the regulations.
- Incorrect recovery of VAT and knowingly.
- Inappropriate processing of VAT inclusive goods and services.
Residential Areas Inclusive of VAT
Article 83 of Executive Regulations stipulates that hotel apartments, ungrounded structures, any place providing bed and breakfast, any tourist complex don’t come under the purview of residential buildings and are subject to usual VAT rates under rules of taxable supplies.
Agent of a Company
Article 19 of Executive Regulation makes it mandatory for any company acting as an agent and working in the name and representing the principal, the agent company must notify the Tax Authority about such arrangement by submitting a power of attorney and including this in its regular scope of activity. The details of principal and beneficiary must also be documented on all the records such as invoices and contracts. The agent must mention a disclaimer on all documents that he is performing all activities on behalf of the principal.
Though enough clarifications are provided in the VAT Executive Regulations, there are still areas needing further clarity. However, the articles specified in the Executive Regulations make it clear that the Tax Authority will be strict and vigilant on the actions of the taxable person. Adherence to these regulations is the key essence as evident in each article.
The introduction of VAT will surely help the country in generating an extra revenue stream though businesses dealing with capital goods may find the market and demand slightly subdued initially. As essential items are mostly kept out of the domain of VAT, it will not put much burden on common Omani citizens.

- Newsletter, Singapore
- March 17, 2021
Singapore’s Digital Economy Partnership Agreement (DEPA) with New Zealand and Chile came into effect on January 7, 2021.
DEPA is a digital-only trade agreement, which aims to establish new ways and collaborations in digital trade issues, promote interoperability of different countries and address new issues caused by digitalization.
First signed in June last year, DEPA is the world’s first of its kind digital trade agreement that establishes a common set of digital trade rules and digital economy collaborations for the removal of digital barriers, fostering a new form of economic engagement especially at a time when many business activities have gone online.
Singapore has been aiming to build on its network of digital cooperation agreements and international frameworks to support businesses and SMEs engaging in cross-border digital trade and e-commerce. Additionally, DEPA will encourage greater cooperation in newly developed areas such as artificial intelligence and provide organizations the capacity to try new technologies across different countries with lower operating costs and better data protection.
Besides this year’s DEPA with New Zealand and Chile, Singapore has also signed DEPA with Australia through the Singapore-Australia Digital Economy Agreement (SADEA), in December 2020. The country is also in exploratory talks with South Korea and the UK to develop a similar bilateral Digital Partnership Agreement.
The Government of Singapore’s DEPA initiatives is in pursuit of further strengthening its footprint as a global leader in technology and e-commerce including the promotion of the country’s extensive free trade agreement (FTA) network for Singapore company formation by foreign investors.
Key Features and Benefits of DEPA
DEPA will establish new and innovative ways to digital trade issues that will help foreign business owners lower the costs of their operations and improve market access with the added advantage for Singapore company incorporation.
Paperless trade
A key feature of DEPA is that it will encourage paperless trade and reduce document transit and cargo clearance time improving business effectiveness.
An exporter in Singapore can easily apply for an e-certificate of origin with an electronic SPS certification for onward transfer to the customs of the destination country.
Paper trades drastically reduce the cost competitiveness and operational efficiency due to the cost of papers and higher waiting time.
Fintech and e-payments
DEPA advocates greater acceptance of payments due to increased interoperability between different payment systems enabling cross-border payments much easier for NBFCs such as fintech firms.
It was in early December last year when Singapore issued its first digital banking license enabling non-bank entities to offer similar services as conventional banks.
Electronic invoicing
DEPA will ensure e-invoices in Singapore are recognized in Chile and New Zealand for shorter invoice processing time, faster payments, and cost savings by embracing similar e-invoicing standards.
Pan-European Public Procurement On-Line (PEPPOL) e-invoicing solutions will also be available in Singapore SMEs.
Digital identities
DEPA will enable countries to develop safe and secure mutually recognizable digital identities that can streamline many business processes such as opening a bank account, registering a company, etc.
Partners within DEPA can facilitate initiatives that promote the compatibility of different digital identity regimes. In doing so, procedures such as Know-Your-Client (KYC) checks by banks can be done more efficiently and in any DEPA partner country, since the bank only requires the company’s digital identity. This due diligence process currently can take over three months to complete.
Data innovation and artificial intelligence
Parties in DEPA will allow data to flow freely across borders which, in turn, facilitates a conducive environment for businesses to develop new products and services from data-driven innovations.
This includes the use of AI for which there will be the adoption of an ethical AI governance framework. This will ensure that DEPA partner countries responsibly harness AI.
Furthermore, this digital agreement means businesses can pilot and commercialize their data-driven products and services with overseas counterparts from DEPA, therefore accelerating cross-border innovation.
Personal data protection
DEPA will ensure greater personal data protection during the transfer of data across borders by developing mechanisms based on international frameworks.
Business organizations in Singapore can now opt for Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation Cross Border Privacy Rules (APEC CBPR) certification and once certified, can demonstrate the company’s strong data protection and security policies consistent with the APEC Privacy norms.
Besides, the CBPR certified companies can exchange data with other certified companies in Singapore’s DEA network, as well as with other regimes which are already certified as per APEC CBPR System.
DEPA will build trust in digital systems facilitating opportunities for participation in the digital economy and promoting the adoption of AI governance framework and responsibly utilizing AI.

- India, Newsletter
- March 17, 2021
In a significant development and approved by the union cabinet, India recently entered into a USD 100 million Defence Line of Credit agreement with Mauritius, the first such pact with an African country as a part of the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA) also called Foreign Trade Agreement (FTA)during a visit by External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar during his visit to Mauritius.
“Privileged to witness along with Prime Minister Pravind Kumar Jugnauth the signing of Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement, India’s first such agreement with an African country. This will help focus on post-pandemic economic recovery and enable business expansion and greater investments,” Mr. Jaishankar said to the media after signing the agreement.
The new framework under the CECPA will allow India a greater entry for Indian goods into the African continent especially for several items including surgical equipment, medicine, and textile products.
A limited agreement by nature, CECPA will cover trade in Goods, Trade in Services, Rules of origin, Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT), Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) measures, Dispute Settlement, Movement of Natural Persons, Telecom, Financial Services, Customs Procedures, and Cooperation in other areas. This will also include 310 export items for India such as foodstuff and beverages, agricultural products, base metals and articles, electrical and electronic items, plastics and chemicals, wood, etc.
“Just to illustrate some of the benefits, Mauritius will get preferential access for export of 40,000 tonnes of sugar into India early frame,” highlighted Mr. Jaishankar. Mauritius will also receive preferential access for the export of 7.5 million pieces of apparel in addition to other 615 products such as frozen fish, specialty sugar, biscuits, fresh fruits, juices, mineral water, beer, alcoholic drinks, soaps, bags, medical and surgical equipment.
A $100 million Defence Line of Credit for Mauritius was also announced. This would “enable the procurement of defense assets from India” according to the requirements of the country which was emerging as an important maritime entity in the Indo-Pacific region. “These initiatives underline once again that the security of Mauritius is the security of India; in the prosperity of Mauritius is our prosperity,” Mr. Jaishankar remarked adding that Mauritius would get a Dornier aircraft and an Advanced Light Helicopter Dhruv on a lease that would help strengthen its maritime security capabilities.
Mr. Jugnauth emphasized that the agreements signed between the two countries would “consolidate the strong ties” between India and Mauritius further and promote foreign direct investment of Mauritius and new Mauritian company formation in India. Notably, during April September 2020, Mauritius ranked 4th in foreign direct investment in India.
The Chagos Archipelago dispute also came up during the discussion, which was an issue of sovereignty and sustainable development before the United Nations. In 2019, India voted for Mauritius at the U.N. General Assembly on this issue. India was amongst the 116 countries that demanded that the U.K. end its “colonial administration” from the archipelago.
“I assured the Prime Minister of India’s steadfast principled support on this issue as has been demonstrated in the past,” noted Mr. Jaishankar.
Me. Jaishankar also reaffirmed India’s medical support to Mauritius in the aftermath of the covid pandemic supported by the recent delivery of 100,000 Covishield vaccines to the African nation. Covid vaccine supply was a “clear and telling demonstration” of the strong bilateral relationship between the two countries, he remarked.
India’s External Affairs Minister also reviewed the status and progress of the India-assisted development projects in Mauritius and invited Mr. Jugnauth for a visit to India.
About business and investment in the services sector, Indian service providers will have access to around 115 sub-sectors from the 11 broad service sectors including computer-related services, research & development, telecommunication, construction, financial, tourism & travel, entertainment, transport, professional services, etc.
India too offered approximately 95 sub-sectors from the 11 broad services sectors, including professional services, R&D, and other business services, and invited Mauritius investors for setting up a company in India.
Both sides have also reached an agreement for an Automatic Trigger Safeguard Mechanism (ATSM) for negotiating on a limited number of highly sensitive products within two years.
India Mauritius bilateral relationship is deep-rooted supported by historic cultural affinities, regular and frequent high-level political interactions, development cooperation, defense and maritime partnership, and people-to-people connection.
Mauritius being an important development partner, India had extended a ‘Special Economic Package’ of USD 353 million to Mauritius in 2016.

- Newsletter, U.A.E
- March 17, 2021
The UAE announced on Saturday, January 30 2021 about the amendment of the country’s citizenship laws granting citizenship status to investors and expatriates for the first time, a move that could potentially benefit the UAE with more foreign investment and new business setup in Dubai. Additionally, the move will mean quality human capital for the country.
The Prime Minister of UAE, Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, also the ruler of Dubai, said “the new measures were aimed at attracting skilled professionals and their families to help in the development of the emirates.”
“We adopted law amendments that allow granting the UAE citizenship to investors, specialized talents & professionals including scientists, doctors, engineers, artists, authors, and their families. The new directives aim to attract talents that contribute to our development journey,” he added.
The nomination and approval rights for qualifying the eligibility of such citizenship will lie with the UAE cabinet, local emiri or rulers’ courts, and executive councils of the seven emirates under clear criteria set for each category. The law will allow those qualified and provided with UAE passports to “keep their existing citizenship”, he added.
The changes to the law on nationality and passports, in effect, will allow expatriates to become dual citizens and for the first time in history for any of the Middle East nations. The UAE has also become one of the few countries in West Asia to grant citizenship to expatriates, who form a large chunk of the population in the region.
The UAE alone is home to millions of foreigners, one of the largest concentrations of expatriates in the Middle East and other parts of West Asia. It is believed that this citizenship amendment act along with the recent Abraham Accord and normalization of diplomatic and economic ties with Israel will witness increased FDI pouring into the UAE with many new Dubai company incorporation as well as many new businesses in other parts of the Emirates.
The categories that can qualify to acquire UAE nationality include.
- Investors
- Specialists
- Families, spouses, and children
- Doctors
- Scientists
- Artists
- Inventors
- Talents
- Intellectuals
Granting of citizenship will be through nominations from the courts of rulers and crown princes, executive councils of the seven emirates, and the cabinet and will be based on nominations received from federal entities.
The UAE cabinet declared the changes in line with an order received from President Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan to attract and retain individuals with specialized skills and innovative minds.
The amendments laid down certain criteria and conditions to be fulfilled by each of the above categories before granting UAE citizenship.
Doctors and specialists must be specialized in a unique scientific discipline or any other scientific principles that are highly required in the UAE and have acknowledged scientific contributions, studies, and research of scientific value and practical experience of not less than 10 years, in addition to obtaining membership of a reputable organization in his/her field of specialization.
Scientists are required to be active researchers at a university, research center, or in the private sector, with practical experience of not less than 10 years. They should have contributions in their field, such as winning a prestigious award or securing substantial funding for research in the past 10 years. It is also mandatory to obtain a recommendation letter from any recognized scientific institution in the UAE.
Investors must own a property in the UAE
Inventors need to obtain one or more patents approved by the UAE’s ministry of economy or any reputable international body, in addition to a recommendation letter from the Economy Ministry.
Persons with creative talents, such as intellectuals and artists, should be pioneers in culture and arts and winners of one or more international awards. A recommendation letter from related government entities is mandatory as well.
If some expatriates qualify then before acquiring citizenship, the expatriates must swear an oath of allegiance, commit to abide by local laws, and inform authorities in case they acquire or lose any other citizenship.
UAE citizenship offers a range of benefits, including the right to establish or own commercial entities and properties, and any other benefits coming into effect from federal authorities.
- Newsletter, Oman
- March 17, 2021
The recent amendment in Oman’s labor laws can be seen as a Government effort to reduce the rights gap between expatriates and locals and this amendment of Foreigners’ Residence Law now enables expatriate workers to transfer jobs without seeking prior approval from their employer; reported a local daily Times of Oman in its press briefing.
The amendment abolished the “No Objection Certificate” (NOC) requirement which, as per the Oman Human Rights Commission, will increase competitiveness between Omani and expatriate workers. This amendment at the same time will also offer protection to low-income families.
The requirement for expatriate workers to obtain a NOC from their current employers to join another company was in force since 2014 under the law of residence for foreigners in Oman. The law required that if a foreigner didn’t secure the NOC from the current employer, the employee was banned from working for any other employee for two years.
The new decision will now enable the foreign employees to switch over to new jobs depending entirely on the lapse of existing work contracts.
The commission added that the decision was also expected to reduce the number of foreign workers leaving the country, who do so because they fail to get NOCs. “The decision will also contribute to reducing the cases of non-Omani labor absconding, especially those who are denied a NOC, thus forcing the worker to stay outside the country after the expiry of his contract,” the commission said in its annual report.
As highlighted by the Times of Oman, the recent amendment is also expected to reduce the gap in wages between local and foreign workers.
“All these legislative and legal amendments, which came in response to the current circumstances, will undoubtedly have a more positive impact on protecting the rights of citizens and residents,” the Oman Human Rights Commission reported.
The policy on Labor Reform was also initiated by Saudi Arabia in November last year mentioning the exceptional situations under which foreign workers were allowed to move to a new job without the prior consent of their present employer.
The scrapping of NOC requirements in Oman can be considered as a significant development in labor laws as this will have a profound impact on the Omani labor market providing much-needed flexibility in changing jobs within the country and foreign workers will find Oman to be more attractive in absence of restrictions.
As Oman continues to attract more foreign talents, many foreign investors are likely to be lured for investments and new company formation in Oman.
Besides labor reforms, digital transformation is also fast happening in Oman and across several ministries and Oman’s fiscal plan announced in November last year also included a number of reforms signalling that business setup in Oman will continue to be easier in post-pandemic time.
A Member Firm of Andersen Global
- 175+ Countries
- 525+ Locations
- 17,500+ Professionals
- 2350+ Global Partners

















 IMC Group
IMC Group